European eel
Eel spend most of thir live in fresh water rivers and ditches. Eels the start and the end of theire lives is in the Sargossa sea, thousends mile from theire freshwater rivers. Like other anguillid eels, European eels have a complex life history, spending most of their life in the “yellow eel” growth phase, during which they inhabit the bottoms of fresh and brackish continental waters. European eels can live more than 50 years in this stage. They are a popular food fish, and have been fished for centuries. But nowadays they are in sharp decline.
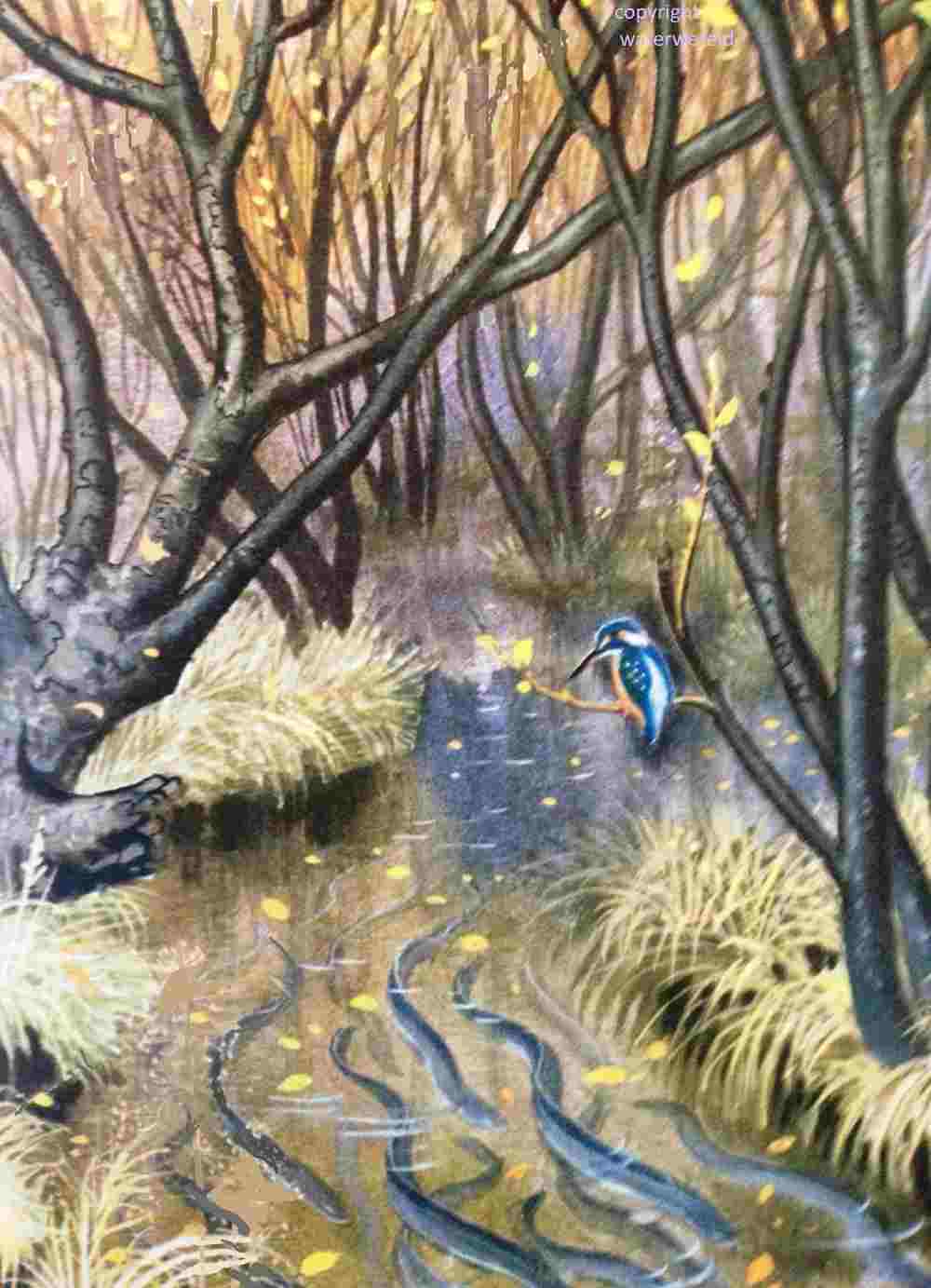

Silver Eels in a wood, observed by a Kingfisher.
Live circle eel
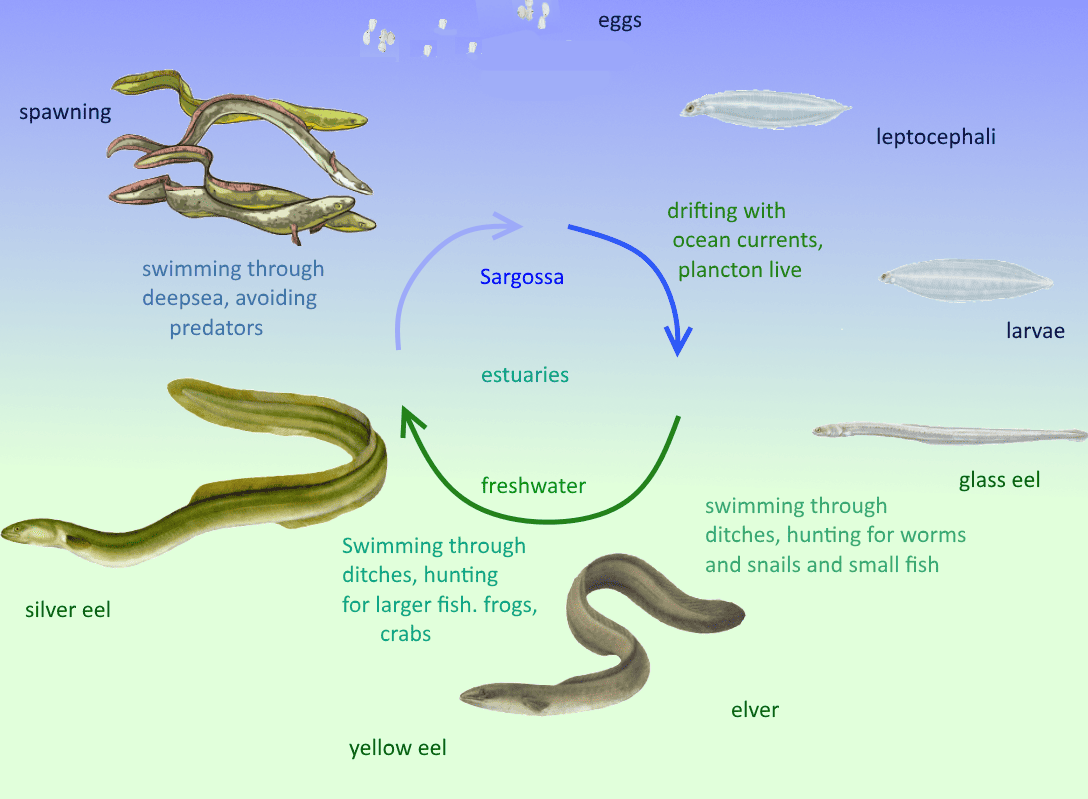
The live circle is fascinating and long : long in time, eels easely reach a livespan of 50 years and more. And a long distance: Europe-Sargasso sea is about 5000 kilometers. it all starts as an egg.
Starting live in the Sargasso sea
The spawning grounds must be in the Sargasso Sea, although no one has ever witnessed eels spawning. The Sargasso sea is the deepest part of the Atlantic, between Bermuda and the West Indies. The larvae must feed on microscopic jellyfish and for a lesser part on copepods, both belonging to the zooplankton. This is concluded as the larvae are often infected by parasitic copepods that are part of the zooplankton. (1)The Sargasso sea is covered with floating yellow seaweed, Sargassum natans and Sargassum fluitans. These floating seaweeds give shelter to the first planctonic stages of the eel.


From the sargasso sea the larvae are drifted to the european estuaries.
The larval stage : becoming glasseels
The larvae, known as leptocephali, are subsequently transported back by ocean currents to continental waters, where the juvenile eels, known as glass eels, enter freshwater bodies or settle in coastal marine areas.

The glass eels leave the ocean and swim upstream into the European continent’s rivers. Hiding in the shadows of eelgrass beds, they grow fat and up to five feet long over 20 years or so before heading back to the Sargasso.
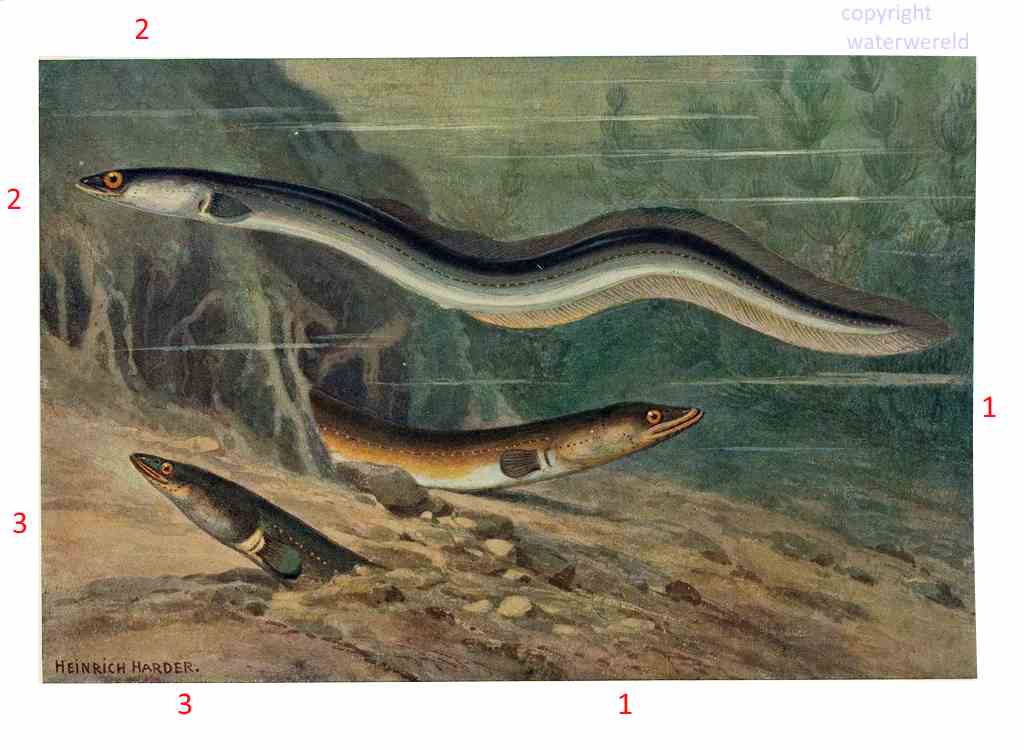

European eel in freshwater changes from color and feeding habits.(6). But eel diet is composed almost entirely of bottom-living organisms: fish , insects larvae, worms , and sometimes even worms that lives ont land , like earth worms.
Starting as a glasseel they started to change color, shape and behavior: They develop a pointed teethed mouth, feeding on crab, (3) or broad mouth , feeding on fish.(1), both are called “yellow eels”, but in German (3) is called “Spitzkopfaal”,and (1) is called: “Breitkopfaal” , It takes some 10 years to become an adult or silvereel (2), in German:”Blankaal”, with their flanks silver colored, their bellies white and with a green back. Nocturnal opportunist carnivores, they eat a broad diversity of fish and invertebrates, like crabs , larger fish and frogs and will also scavenge on dead organisms. The silver eels start to swim to the sea and start the big journey back to the Sargasso Sea , only to spawn there. During this period they don’t eat , and live on bodyfat.
Back to the Sargasso sea
It takes one year to swimm back the 5000 kilometers . During the night, they swim in shallow water, at a level between 200m below the surface. In the morning they dive to 1000 meter depth or more, this way avoiding most of the predators.
Spawning in the Sargasso
Spawning must take place at greath depth, although no one has ever witnessed eels spawning. Soon after spawning the eels die.
The European eel is endangered
Reference
1 Are eels (Anguilla anguilla sp) planctonic feeders? Evidence from parasite communities C. R. Kennedy, P. Nie, J. Kaspers, J. Paulisse
4 painting by
6 painting by Heinrich Harder
